 |
| Jurong Island |
Wednesday, 1 January 2014
Mass Transfer
Gas-Liquid Mass Transfer:
Ever wonder how do petrochemical industries reduce their air pollutions emitted by their machinery to abide by the laws imposed on them and to prevent acid rain/global warming? This is done by using a unit operation called the Gas-Liquid Mass Transfer using the Gas Absorption towers.
So what does Gas Absorption towers do?
It involves 2 phases (gas and liquid) which are brought together intimately with the presence of packing in the tower, where the solute will diffuse from the gas phase to the liquid phase. Basically this means that the gas that is harmful will be diffused into the liquid so that it is extracted out when the industrial machine releases the gases.
Liquid-Gas Mass Transfer:
Whenever a heat exchanger is used, there will be warm water that will be discharged. As the warm water has to be cooled down before sending it back to the heat exchanger. This is achieved by using a unit operation called the Liquid-Gas Mass Transfer by using cooling towers.
So what does Cooling towers do?
A cooling tower is just like a condenser that you use in a lab. The driving force of gas phase is due to difference in humidity where water evaporates to gas phase by latent heat of evaporation. The driving forces for the temperature in the liquid phase and for the gas phase. The sensible heat will be transferred from the bulk liquid to the interface in the liquid and from the interface to bulk gas. In simple terms, the water phase is cooled down as water vapour diffuses into the gas phase by evaporating.
Ever wonder how do petrochemical industries reduce their air pollutions emitted by their machinery to abide by the laws imposed on them and to prevent acid rain/global warming? This is done by using a unit operation called the Gas-Liquid Mass Transfer using the Gas Absorption towers.
So what does Gas Absorption towers do?
 |
| Packings for Gas Absorption |
 |
| Gas Absorption Towers |
Liquid-Gas Mass Transfer:
Whenever a heat exchanger is used, there will be warm water that will be discharged. As the warm water has to be cooled down before sending it back to the heat exchanger. This is achieved by using a unit operation called the Liquid-Gas Mass Transfer by using cooling towers.
So what does Cooling towers do?
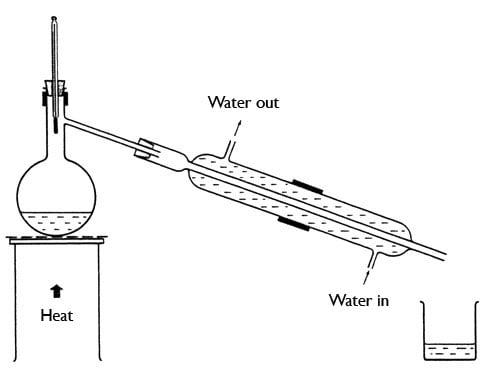 |
| Condenser attached to a boiling flask |
 |
| Trays for Cooling Towers |
 |
| Cooling Tower |
What do Chemical Engineers do?
Chemical engineering is the relationship between molecular sciences and engineering. In the past, fuel combustion and energy systems is usually related to chemical engineering. However, present chemical engineers are spearheading new developments in manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, healthcare, design and construction, pulp and paper, petrochemicals, food processing, specialty chemicals, microelectronics, electronic and advanced materials, polymers, business services, biotechnology, and environmental health and safety industries. So if you are interested in venturing into any of these industries, you may want to consider have a Diploma in Chemical Engineering after your 'O' Levels if you are planning to go to a Polytechnic!
What do Chemical Engineers do?
- Chemical engineers involve in the process of refining petroleum products, making energy and chemical sources more productive and cost effective.
- Chemical engineers also help to improve food processing techniques and methods of producing fertilizers, in order to improve both the quantity and quality of the food. They also help to develop solution to environmental problems such as pollution control.
- Chemical engineers face many of the same challenges that other professionals face, and they meet these challenges by applying their technical knowledge, communication and teamwork skills; the most up-to-date practices available; and hard work. Benefits include financial reward, recognition within industry and society, and the gratification that comes from working with the processes of nature to meet the needs of society.
What are the criteria needed?
You need to excel in mathematics and science in order to be a chemical engineer because to overcome technical problems safely and economically, chemical engineers rely on their knowledge on mathematics and science.
What do Chemical Engineers do?
- Chemical engineers involve in the process of refining petroleum products, making energy and chemical sources more productive and cost effective.
- Chemical engineers also help to improve food processing techniques and methods of producing fertilizers, in order to improve both the quantity and quality of the food. They also help to develop solution to environmental problems such as pollution control.
- Chemical engineers face many of the same challenges that other professionals face, and they meet these challenges by applying their technical knowledge, communication and teamwork skills; the most up-to-date practices available; and hard work. Benefits include financial reward, recognition within industry and society, and the gratification that comes from working with the processes of nature to meet the needs of society.
What are the criteria needed?
You need to excel in mathematics and science in order to be a chemical engineer because to overcome technical problems safely and economically, chemical engineers rely on their knowledge on mathematics and science.
Our Role
 Our role in the future is to be in the Research and Development sector of Chemical Engineering where we wish to work in a renown company such as Institute of Chemical and Engineering Sciences (ICES) that is an autonomous national research institute under A*STAR (Agency for Science, Technology and Research). ICES was established in 2002 and carries out world class scientific research, develops novel technology and nurtures creative scientists and engineers to support Singapore's chemical, biomedical and process engineering industries.
Our role in the future is to be in the Research and Development sector of Chemical Engineering where we wish to work in a renown company such as Institute of Chemical and Engineering Sciences (ICES) that is an autonomous national research institute under A*STAR (Agency for Science, Technology and Research). ICES was established in 2002 and carries out world class scientific research, develops novel technology and nurtures creative scientists and engineers to support Singapore's chemical, biomedical and process engineering industries. Why Research & Development?
We would like to venture out into R&D sector because there are many devices, machinery and fuel that can be improved on. Such as researching to produce petroleum and diesel to have the lowest pollution emitted by vehicles to slow down global warming; to develop a heat exchanger with the best efficiency so that energy won't be wasted; to research and develop the best packings and trays for a faster and more efficient gas absorption operations and cooling tower operations.
Why ICES specifically?
As ICES has the latest technology that also specialises the chemical industry. This will enable us as chemical engineers to have the best work experience at hand with other experienced scientist.
In the Chemical Industry
There are different chemical industry jobs situated at Jurong Island. There are many companies present such as: BASF, ExxonMobil, Lanxess, Mitsui Chemicals, Shell, Sumitomo Chemicals, etc.
There are many Research and Development sectors located in Jurong Island. It has a diverse range of activities from exploratory research to process development, optimisation and problem solving as well as the running of pilot-scale projects.
Job Opportunities:

1. Workplace Safety and Health Officer (Part Time and Full Time): Where their hours, depending on full time or part time will be used for safety supervision and safe conduct of work. They are able to work in shipyards, factories manufacturing garments or factories handling timbre and petroleum products.
2. Process Plant Technician: Prepare and measure raw materials; Feed raw material and processing agents into plant machinery; Set controls and operate machinery; Check instruments and equipment to make sure of correct operation, and attend to any abnormal operating conditions; and take samples for testing, test products and record process data.
3. Manufacturing Industry: Manufacture goods and products used by customers.
4. Quality Control Lab Assistant: Performing tests in a laboratory environment can include analysis, assembling and disassembling, and attempting destruction or chemical variations of products to ensure quality. Results are then reported to help improve manufacturing processes.
5. Environmental Assistant: An environmental assistant is a position of manual labour in which an employee works to clean or physically improve the workplace environment. In some emerging job descriptions, it is a "green" career in which the employee works toward helping the environment in a community- and world-wide sense.
6. Nanotechnology: Structures, devices, and systems having novel properties and functions due to the arrangement of their atoms on the 1 to 100 nanometer scale. Many fields of endeavor contribute to nanotechnology, including molecular physics, materials science, chemistry, biology, computer science, electrical engineering, and mechanical engineering.
7. Material Technologist: Materials technicians test the behaviour of materials under different conditions, in a range of industries. The results of these tests are used by companies to improve the performance of existing products, to eliminate faults with materials already in use, and to help with the development of new technologies.

8. Petrochemical Engineers: is involved in nearly all stages of oil and gas field evaluation, development and production. The aim is to maximise hydrocarbon recovery at minimum cost while maintaining a strong emphasis on reducing environmental impact.
Job Opportunities:

1. Workplace Safety and Health Officer (Part Time and Full Time): Where their hours, depending on full time or part time will be used for safety supervision and safe conduct of work. They are able to work in shipyards, factories manufacturing garments or factories handling timbre and petroleum products.
2. Process Plant Technician: Prepare and measure raw materials; Feed raw material and processing agents into plant machinery; Set controls and operate machinery; Check instruments and equipment to make sure of correct operation, and attend to any abnormal operating conditions; and take samples for testing, test products and record process data.
3. Manufacturing Industry: Manufacture goods and products used by customers.
4. Quality Control Lab Assistant: Performing tests in a laboratory environment can include analysis, assembling and disassembling, and attempting destruction or chemical variations of products to ensure quality. Results are then reported to help improve manufacturing processes.
5. Environmental Assistant: An environmental assistant is a position of manual labour in which an employee works to clean or physically improve the workplace environment. In some emerging job descriptions, it is a "green" career in which the employee works toward helping the environment in a community- and world-wide sense.
6. Nanotechnology: Structures, devices, and systems having novel properties and functions due to the arrangement of their atoms on the 1 to 100 nanometer scale. Many fields of endeavor contribute to nanotechnology, including molecular physics, materials science, chemistry, biology, computer science, electrical engineering, and mechanical engineering.
7. Material Technologist: Materials technicians test the behaviour of materials under different conditions, in a range of industries. The results of these tests are used by companies to improve the performance of existing products, to eliminate faults with materials already in use, and to help with the development of new technologies.

8. Petrochemical Engineers: is involved in nearly all stages of oil and gas field evaluation, development and production. The aim is to maximise hydrocarbon recovery at minimum cost while maintaining a strong emphasis on reducing environmental impact.
What is Chemical Engineering?
 |
| Jurong Island |
Chemical Engineering is a discipline involving numerous areas of technology. Basically, Chemical Engineering is a branch of chemistry and engineering that applies the physical sciences (e.g., chemistry and physics) and/or life sciences (e.g. biology, microbiology and biochemistry) together with mathematics and economics to production, transformation, transportation and proper usage of molecules, chemicals, materials and energy.
What is Unit Operation?
 |
| Heat Exchanger |
So what is Unit Operation?
Firstly, unit operation is the operation that involves basic physical operations of chemical engineering in a chemical process plant, that is distillation, fluid transportation, heat and mass transfer, evaporation, extraction, drying, crystallization, filtration, mixing, size separation, crushing and grinding, and conveying.
Distillation is a unit operation that is used to purify or
separate alcohol in the brewery industry.
The same distillation separates the hydrocarbon in a
petroleum industries.
Flow of liquid hydrocarbon in a petroleum refinery and flow
of milk in a daily plant for the solidification in spray dryer.
What are the many different Unit Operations?
 |
| Crystallization |
solute such as a salt from solution by precipitation in the industries for large scale operations, electrostatic precipitation is operated for this concept.
2. Fluid Flow: Concerns the principle that determine the flow or transformation of fluids from one point to another. The fluid can be a liquid or a gas. (Bernoullie's equation)
3. Heat Transfer: Deals with principles that govern accumulation and transfer of heat and energy from one place to another. The three concepts followed here are conduction, convection and radiation.
4. Evaporation: A special case of heat transfer which deals with the evaporation of volatile solvent such as waste from a non-volatile solute such as salt or any other material in the solution. Example: The evaporation of trichloro-ethylene a cleaning agent in the automobile service industry and acetone in the case of glassware in a chemical process industries follow this unit operations.
5. Drying: An operation in which volatile liquids (usually water) are removed from solid material.
6. Distillation: An operation where a components of the liquid mixture are separated by boiling because of their difference in vapour pressure.
7. Absorption: A process whereby a component is
removed from gas mixture by treatment with liquid.
8. Liquid-Liquid Extraction: A process in which a solute in a
liquid solution is removed by contact with another liquid solvent that is
relatively irreversible with solution.
9. Liquid-Solid Leaching: It
involves treating a finely divided solid with a liquid that dissolves and
removes a solute contain in the solid.
10. Mechanical physical separation: This involves separation
of solids, liquids or gases by mechanical means such as filtration, settling,
size reduction which are classified as separate unit operations.
The outline of unit operation defines the settling tanks for
sedimentation, filter press for separations, pressurized spheres for ammonia
storage, palletising for fertilizer compounds, pneumatic conveyors for cement
industry, bucket wheel elevators for
thermal power stations and belt conveyors for core industries and many more in
operation.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

